Revolutionary Wireless Implant Could Transform IBD Treatment Through Neural Stimulation

Summary of EurekAlert!
IBD Movement provides news analysis and insights for the IBD community. Always consult your healthcare provider for personal medical advice.
A New Dawn for IBD Management
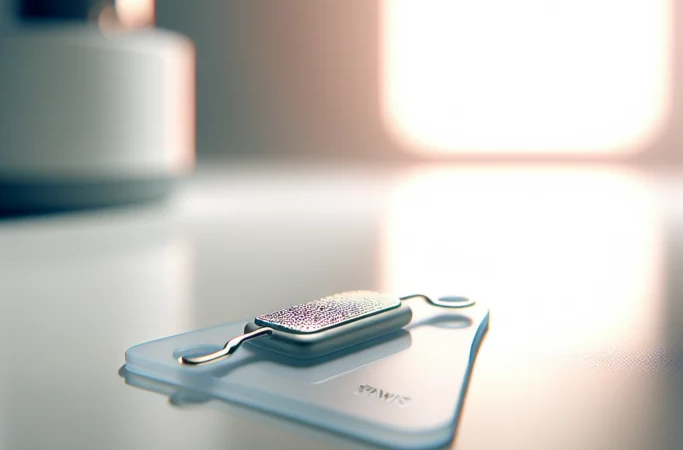
Imagine a future where managing your inflammatory bowel disease doesn’t require daily medications with concerning side effects, but instead relies on a tiny, wireless device that works with your body’s own healing mechanisms. This vision may be closer to reality than you think. Groundbreaking research has unveiled a soft, wireless implant that treats inflammatory bowel disease by tapping directly into the body’s neural network, potentially revolutionizing how we approach IBD care.
For the millions of people living with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis worldwide, this development represents more than just another treatment option—it could be the key to achieving sustained remission without the immunosuppression, injection fatigue, or medication failures that so many of us know all too well.
Breaking Down the Research
According to EurekAlert!, researchers have developed an innovative wireless implant designed specifically to treat inflammatory bowel disease through neural stimulation. This soft, biocompatible device represents a significant advancement in bioelectronic medicine, offering a new therapeutic pathway that works by interfacing with the body’s existing neural networks to modulate inflammatory responses.
The implant operates without the need for external wires or frequent surgical interventions, making it a potentially more patient-friendly option compared to traditional electronic medical devices. By targeting the neural pathways involved in inflammation control, this technology aims to reduce intestinal inflammation at its source, rather than simply suppressing the immune system broadly as many current IBD medications do.
The research team’s approach focuses on leveraging the body’s natural anti-inflammatory mechanisms through precise neural stimulation, potentially offering a more targeted and sustainable treatment approach for people with IBD. This wireless capability means the device can function autonomously once implanted, reducing the burden on patients for ongoing maintenance or external device management.
What This Could Mean for Your IBD Journey
This breakthrough represents a fundamental shift in how we might approach IBD treatment in the coming years. For those of us who have navigated the complex world of biologics, immunomodulators, and steroids, the concept of a device that works with our bodies rather than suppressing our immune systems is genuinely exciting.
The implications for daily life could be transformative. Consider the freedom from injection schedules, the relief from medication-related anxiety, and the potential for achieving remission without the constant worry about infection risk that comes with immunosuppressive therapies. This neural approach could offer sustained symptom control while preserving your body’s natural ability to fight infections and heal wounds.
What makes this particularly promising for the IBD community is the precision of neural stimulation. Unlike systemic medications that affect your entire body, neural stimulation can be targeted specifically to the areas and pathways involved in intestinal inflammation. This specificity could mean fewer side effects and more predictable outcomes—two things that anyone who has tried multiple IBD treatments knows are incredibly valuable.
The wireless nature of this implant also addresses one of the major concerns many patients have about medical devices: the need for frequent procedures or external components that might interfere with daily activities. A fully implanted, wireless system could potentially allow you to swim, travel, exercise, and live your life without the constant awareness of your medical treatment that characterizes so many current IBD therapies.
For people who have experienced medication failures or developed antibodies to biologics, this technology could represent a entirely new therapeutic avenue. The mechanism of action is so different from current treatments that it might offer hope even for those with treatment-resistant disease patterns.
However, it’s important to consider the questions this technology raises. How would the implant be monitored? What happens if it needs adjustment or replacement? How would this interact with other IBD treatments you might need? These are the kinds of practical considerations that will need to be addressed as this technology moves through clinical trials.
The potential for personalized treatment is also significant. Neural stimulation parameters could potentially be adjusted based on individual response patterns, disease severity, and specific inflammatory markers. This level of customization could help address the frustrating reality that IBD affects everyone differently, and what works for one person may not work for another.
Expert Perspectives on Neural Stimulation
The field of bioelectronic medicine has been gaining momentum in recent years, with experts increasingly recognizing the potential of neural stimulation for treating inflammatory conditions. Medical professionals specializing in IBD treatment are cautiously optimistic about these developments, noting that neural approaches could complement existing therapies rather than replace them entirely.
Gastroenterologists emphasize that while this technology is promising, it will likely require extensive clinical trials to establish safety profiles and efficacy compared to current standard treatments. Patients interested in this development should discuss with their healthcare teams how emerging technologies might fit into their long-term treatment plans and whether they might be candidates for clinical trials as they become available.
What You Can Do Now
- Stay informed about clinical trials: Research institutions may begin recruiting patients for studies involving neural stimulation devices for IBD in the coming years
- Discuss emerging treatments with your gastroenterologist: Ask about bioelectronic medicine and how it might fit into your treatment strategy
- Document your current treatment responses: Detailed records of what has and hasn’t worked for you could be valuable if you become a candidate for innovative therapies
- Connect with IBD research communities: Organizations like the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation often provide updates on cutting-edge research developments
- Maintain optimal health while waiting: Continue following your current treatment plan and working with your healthcare team to achieve the best possible disease control with available therapies
Looking Toward a Brighter Future
While this wireless implant technology is still in development, it represents the kind of innovative thinking that gives the IBD community real reason for hope. The shift toward precision medicine and bioelectronic approaches could fundamentally change how we experience life with inflammatory bowel disease.
This development reminds us that researchers around the world are working tirelessly to improve outcomes for people with IBD. Each breakthrough, whether it’s a new medication, a novel device, or a better understanding of disease mechanisms, brings us closer to a future where IBD doesn’t define the boundaries of what’s possible in our lives.
As we await more detailed study results and clinical trials, let’s continue supporting each other and staying engaged with the latest research. What questions do you have about this neural stimulation approach? How do you think it might fit into the evolving landscape of IBD treatment? Share your thoughts and join the conversation about the future of IBD care.
Source: This post summarizes reporting from EurekAlert!. Read the original article.